MD7005: Clinical trial data analysis Assignment help

Question
MD7005: In this University of Chester Assignment, the student is required to write a a clinical trial research report. The purpose of the assessment is to evaluate the student’s clinical knowledge, reasoning, and interpretation abilities. It has been remarked that two novel medications, ciptinib and imatinib were randomly assigned to 100 newly diagnosed CML patients. The patients underwent five years of follow-up, for which the medical trial data report has been provided to the student. Based on a thorough analysis of this data, a a clinical trial research report needs to be developed.
Solution
Using the data from the clinical study, our experts have written a comprehensive clinical report. In providing Biomedical Science Assignment Help for this report, our experts have presented Imatinib and Ciptinib comparative Clinical Trial Study in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia.
Introduction
Our experts have written a brief introductory paragraph defining the terms CML and CIP2A. The definition have been taken from relevant, credible sources. This is how our experts provide the best MSc assignment help in the UK.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) is a hematological malignancy characterized by a genetic anomaly known as the Philadelphia chromosome, initially identified in 1960 by Nowell and Hungerford (Nowell & Hungerford, 1960). This chromosomal alteration leads to the formation of an abnormal protein called BCR-ABL. triggering uncontrolled growth of myeloid cells. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) has undergone a transformative shift in its therapeutic landscape with the advent of Imatinib, as supported by Aichberger et al. (2007) and Branford et al. (2003), a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) that effectively targets the BCR-ABL fusion protein in CML, which plays a pivotal role in driving the uncontrolled growth of myeloid cells. Hochhaus et al. (2017) and Jabbour et al. (2011) have extensively discussed the long-term outcomes of Imatinib treatment, highlighting its success in achieving deep and sustained molecular responses, significantly improving patient prognosis. Radich et al. (2006) and Shoumariyeh and von Bubnoff (2014), and Kim et al. (2010) have emphasized its role in overcoming resistance and intolerance observed with earlier therapies. However, despite the remarkable advancements in CML management, there remains a subset of patients who experience treatment failure over the long term.
If you are searching for Biomedical Science Assignment Help in England, you are at the right place. Call us at +61 871501720.
Methods
The following section discusses the Table of characteristics for patients, meanings of MR4 and progression free survival, and tests of statistics which are important here. This section is further divided into three sub-sections:
Patient characteristics table
The study included a cohort of 100 patients who were evenly assigned to receive either imatinib or Ciptinib. Moreover, patients were categorized into high and low CIP2A expression groups based on their symptomatic CIP2A protein levels (Mean Fluorescence Power (MFI)). High CIP2Alevels were characterized as those in which CIP2A levels (MFI) were equal to or greater than 10. The patients were closely observed until specific events (e.g., death, disease progression to blast crisis, or completion of the 60-month observation). Table 1 outlines patient demographics and clinical characteristics.
Definitions of progression free survival and MR4
PFS is a critical endpoint in clinical trials, particularly in the context of treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). It measures the duration from the initiation of treatment until the occurrence of specific events that indicate disease progression, relapse, or mortality from any cause. In the context of CML, disease progression may manifest as various factors, including but not limited to a rise in the count of leukemic cells, the emergence of new symptomatic or complication-related issues, or the transition of the disease to a more advanced and potentially incurable stage.
Statistical tests
For the statistical analysis, we utilized the SPSS statistical software. Descriptive statistics, such as the median, interquartile range, and range, were employed to summarize continuous data, while categorical data was expressed as frequencies and percentages.
Get MSc Biomedical Science assignment help at 25% off. WhatsApp us at +447700174710 today!

Results
The next section provides a detailed outline of the results derived from the analysis done by our experts above. We have provided a snippet of the complete results for your reference here:
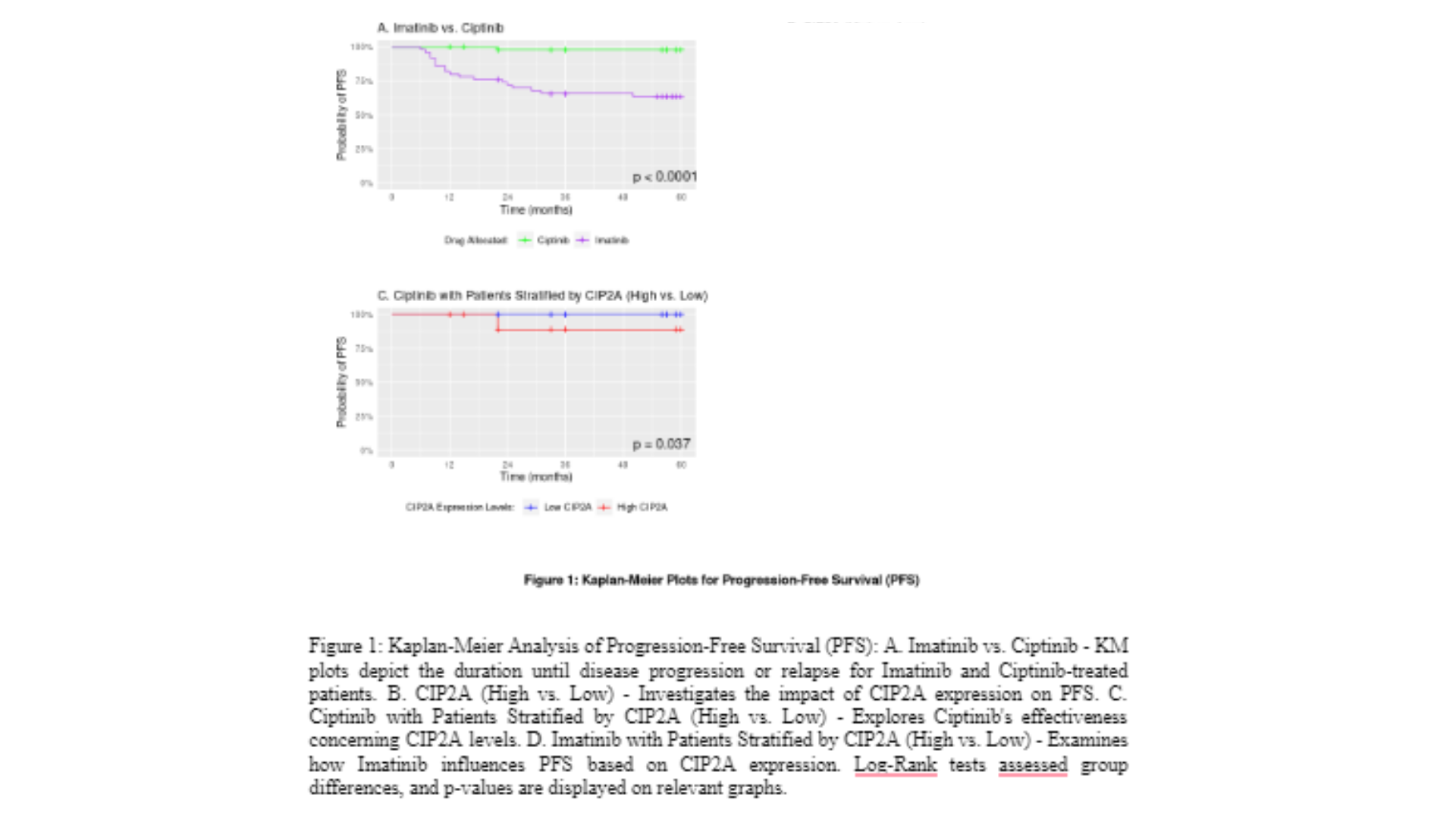
Figure 1A displays the Kaplan-Meier (KM) plot for progression-free survival (PFS) comparing Imatinib and Ciptinib in terms of probability of patients in each treatment group remaining free from the disease progression over the 5 years of follow up. The statistical analysis using the stratified log-rank test demonstrated a significant difference in the PFS between Ciptinib and Imatinib (log-rank test statistic = 18.33, p-value < 0.0001), suggesting that the two treatments have distinct effects on disease progression in patients with CML. The two curves start to separate at 6 monthsof follow-up, with a more pronounced divergence at 8 months. The Imatinib curve shows a decline in PFS, reaching a value of 64% by the end of the follow-up period. In contrast, the Ciptinib curve remains relatively constant, with a PFS rate of 98% at the end of the follow-up. The estimated means further support the superiority of Ciptinib, with a mean PFS of 59.21 months (STD = 0.78) compared to 44.35 months (STD = 3.1) for Imatinib. The median follow-up duration was not reached for either treatment group, suggesting that a significant proportion of patients remained free from disease progression throughout the study. Therefore, based on these findings, it can be concluded that Ciptinib is the more effective treatment option, demonstrating superior efficacy in terms of prolonging PFS compared to Imatinib. The KM plots in Figure 1B for high and low CIP2A expression in terms of progression-free survival (PFS) reveal substantial differences between the two groups. The log-rank test statistic of 75.16 associated with a p-value of < 0.00001 indicates a highly significant separation of PFS outcomes based on CIP2A expression. The separation of the curves becomes apparent after 6 months of follow-up, with a notable divergence at 8 months. The high CIP2Acurve demonstrates a decline in PFS, reaching a value of 34.5% by the end of the follow-up period. Conversely, the low CIP2A curve remains consistently high, with a PFS rate of 100% at the end of follow-up. The estimated PFS at 50% and 75% for high CIP2A are 23 months (std error of 4.7) and 11 months (std error of 1.5), respectively.
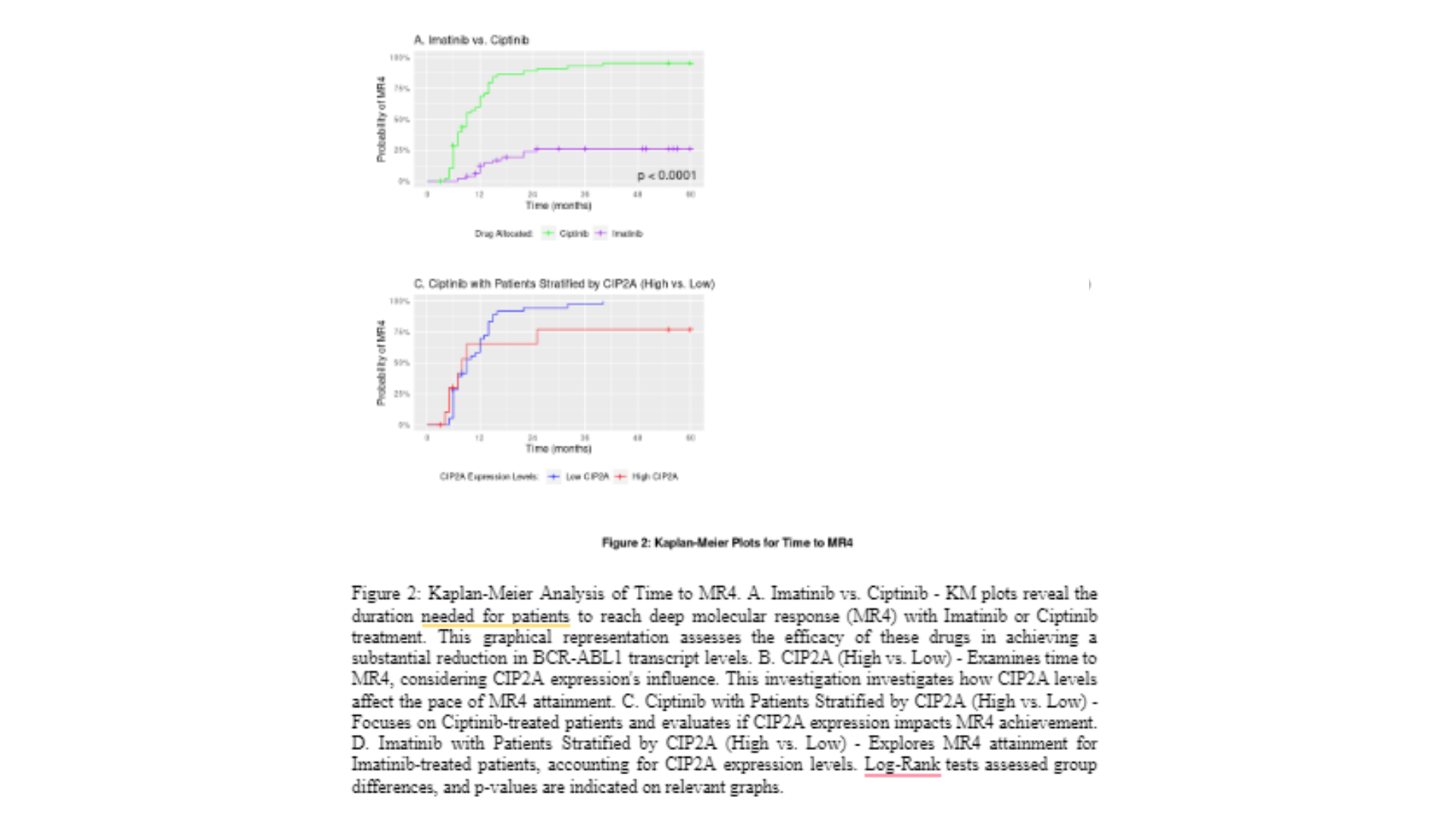
The KM plots in Fig 2A for achieving MR4 in patients treated with Imatinib and Ciptinib reveal substantial differences in treatment outcomes. The log-rank test statistic of 62.63 and a p-value of < 0.0001 indicate a highly significant separation of the MR4 achievement curves. After 6 months of follow-up, the curves begin to diverge, with the Imatinib curve showing a slow rise and only reaching 24% of patients who achieved MR4 at the end of the follow-up. In contrast, the Ciptinib curve continues to rise steadily, with 88% of patients achieving MR4 by the end of follow-up. These findings suggest that Ciptinib is more effective in promoting MR4 achievement compared to Imatinib. The substantial difference in MR4 rates between the two treatment groups indicates that Ciptinib may offer superior therapeutic benefits in terms of achieving deep molecular responses in patients with CML.
Are you looking for Biomedical Science Assignment Help in England? Get in touch with our experts today! Reach out today- onlineassignmentservices1@gmail.com.
Discussion
Here, the results derived above are discussed in non-clinical language for better understanding by the readers. Through structuring the report in accordance with the assessment file, OAS experts assure high-quality University of Chester Assignment Help.
Our study aimed to compare the effectiveness of Imatinib and Ciptinib in the treatment of CMLand to investigate the impact of CIP2A expression on treatment outcomes. We conducted a thorough survival analysis using Kaplan-Meier plots, with progression-free survival (PFS) and achieving a deep molecular response (MR4) as primary endpoints. A significant difference in progression-free survival (PFS) was identified between patients treated with Imatinib and those treated with Ciptinib. This finding is in line with previous research by Lucas et al. (2015) and Lucas et al. (2011), emphasizing the potential of CIP2Ainhibition in preventing disease progression and improving outcomes in high-risk CML patients. It’s important to note that CML treatment has evolved over the years with the introduction of various tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), and our results align with the observed superior efficacy of newer agents such as Ciptinib. The influence of CIP2A expression on PFS is a critical aspect of our study. High CIP2Aexpression was associated with a shorter PFS compared to low CIP2A expression.
Want to order MD7005 Clinical trial data analysis Assignment help? Let us help you. Call us at +61871501720 to read more.

