BLAW1002: Economics Principles Analysis Assignment Help

Question
BLAW1002: This is a Question-and-answer-based Economics Analysis assignment for Curtin University Australia. This Business law assignment urges the student to explore the monopolistic company’s ability to exert influence by driving up prices and increasing retail markups. The assignment demands the student to imagine themselves in the role of a manager, entrepreneur, and economist owning a retail firm in the competitive restaurant and food service industry. It is remarked that facing an increase in marginal costs, the prices were raised by 35%. This move aligns with competitors adjusting prices. The student is required to answer the questions based on this case study for a food restaurant.
Solution
The solution to this assignment includes the answers to all the EPA questions of the assignment. To get answers to your study questions for blaw1002 written by our highly qualified experts, you can reach out to OAS as well!
Question 1
In the first question, a detailed explanation and comparison of the profit and markup in Diagrams 1 and 2 is presented based on the case study and economic theory. Our experts elevate our Business law assignments by incorporating important theoretical concepts of Economics in the answers to all the questions.
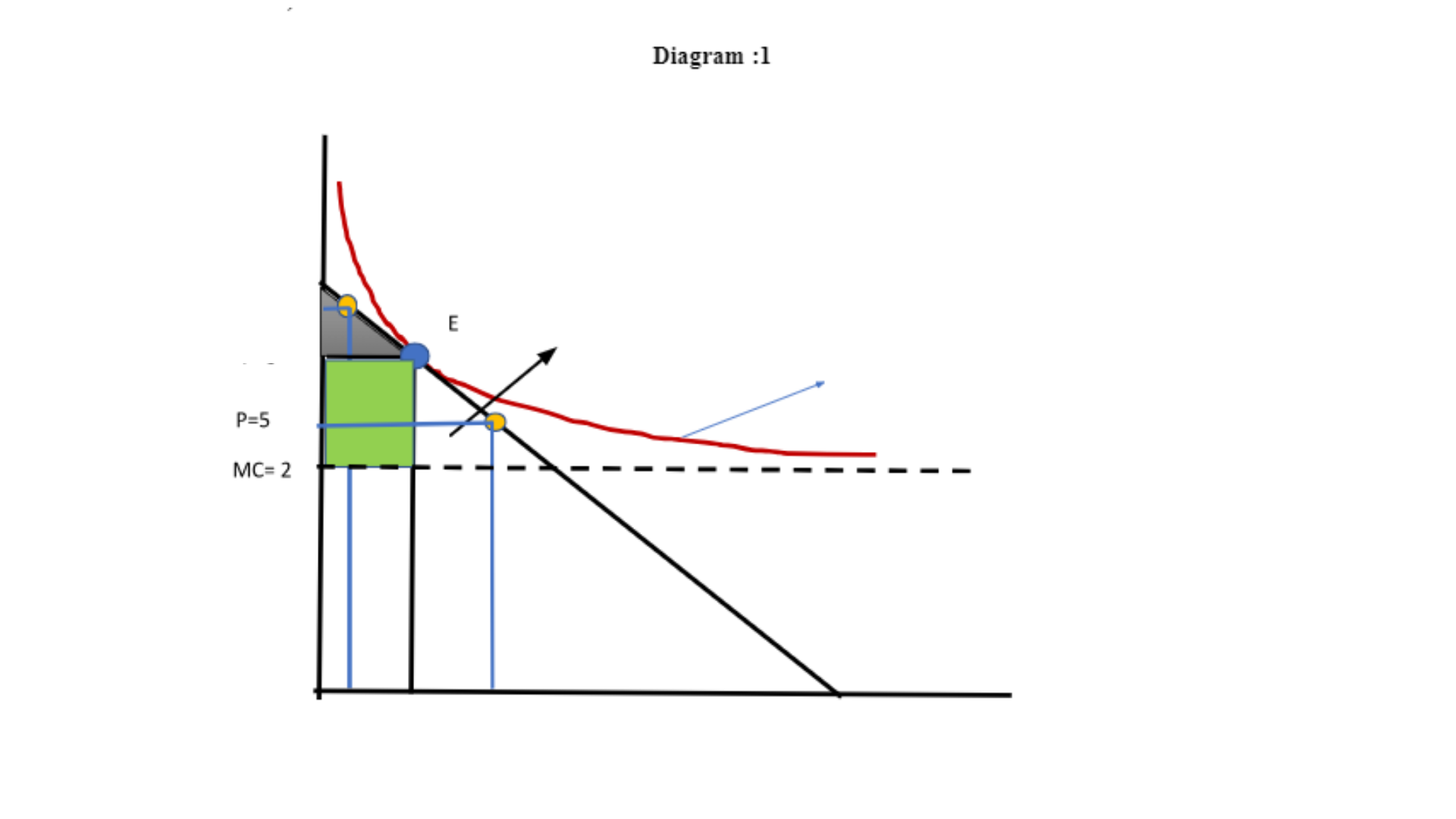
Isoprofit curve is very similar to indifference curve. Utility level remains the same along the indifference curve. Similarly, when we join the points on isoprofit curve, the level of total profit remains the same. Isoprofit curve can be considered as the owner’s indifference curve where the owner is indifferent between the hypothetical combination of price and quantity that offers her the same level of profit. The demand curve shows the willingness to pay for the consumers. The consumers who are willing to pay $6 and more will buy and receive a surplus. Consumers who has the willingness to pay at $6 , will buy but receive zero surplus. If the willingness to pay is greater than the actual price $6, then the consumer will receive a surplus. Similarly, if the price paid by the consumer is higher than the cost, then the firm receives a surplus. The area above the price is called the consumer surplus. This surplus can be obtained by adding the surplus of each buyer. On the other hand, the area below the price is called the producer surplus. The share of surplus for the producer is greater than the buyer. (coreecon n.d.).
If they serve 20,000 students, then the profit will be,
Profit =Q * P – Q* MC
Profit =Q * (P-MC)
Profit=20,000 (6-2)
Profit=20,000 * 4
Profit = 80000
Let us identify anyone price/quantity point to the left and any one price/quantity to the right of the price $6 as set the restaurant.
We must find other combinations in the demand curve that would give the same level of profit of $80000.
P=7
Q(7-2) =80000
5Q = 80000
Q= 14000
Thus (7,14000) is one combination to the left of point E, that gives the same level of profit 80000.
When P= 5,
Q (5-2) =80000
3Q=80000
Q= 80000/3= 26666.67
Thus (5, 26666.67) is another combination to the right of point E, that gives the same level of profit 80000.
Do you also need the BLAW1002 Markets And Legal Frameworks Assignment Sample for students of Curtin University? Let us help you. Reach out today- onlineassignmentservices1@gmail.com.
Question 2
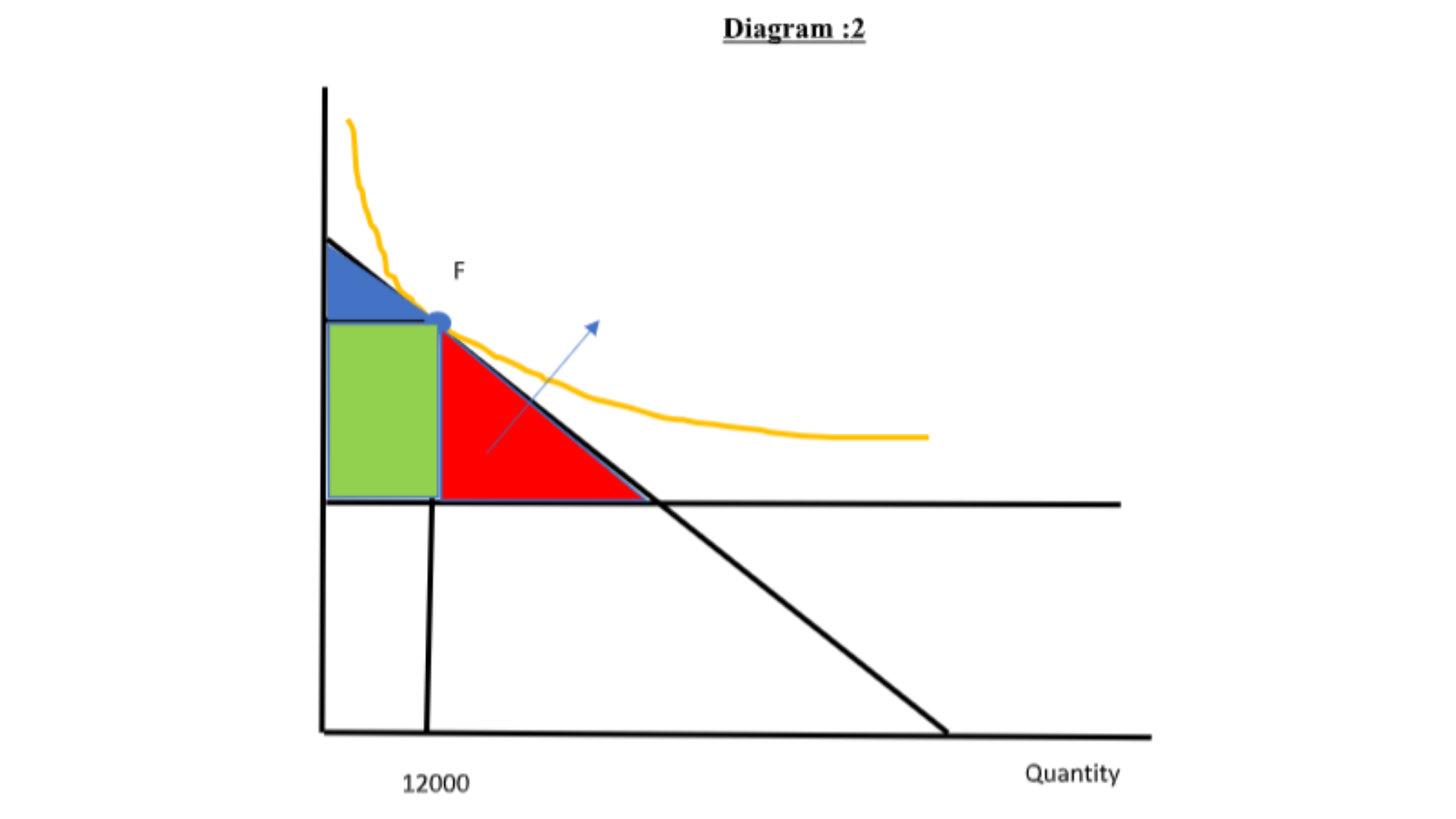
This question requires the student to imagine the consequences if the company implemented a strategic pricing control to match that of a competitive market. The price and amount that would be sold in diagram 2 have been explored in detail in this section by our experts.
If strategic price control is put in place reflecting a competitive market, then the price will become equal to MC.
The firm will charge P= $2.3
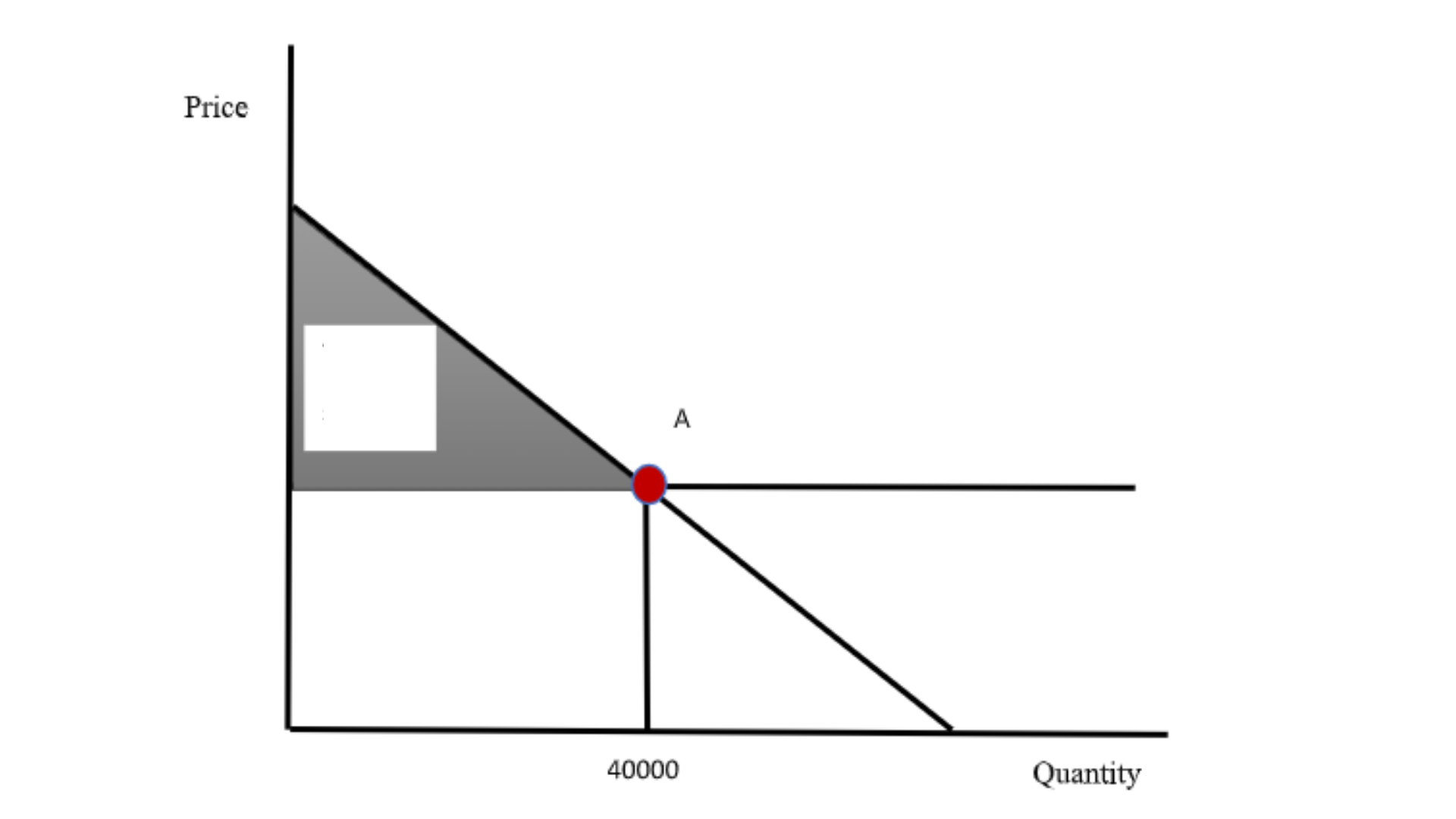
When the competitive price is charged, the shaded area shows the total surplus. The entire surplus is the consumer surplus. Consumers will be better off and there will a significant gain in consumer surplus the firm is at point A, rather than point F. Since price becomes equal to marginal cost, there will be no producer surplus. At point F, there will be loss in consumer surplus, though there was some gain in producer surplus. But the magnitude of the loss of consumer surplus is higher than the magnitude in the gain in producer surplus, leading to deadweight loss. Since the firm is asked to charge competitive price, a greater number of customers will be willing to buy. Now the firm will get 40000 customers with the price of 2.3
If you are also looking for the best assignment help services in Australia, reach out to OAS via WhatsApp at +447956859420.
Question 3
In this section, our experts have responded to the question of the current price elasticity or inelasticity of demand for the empanadas. Our experts have discussed the pertinent information about the price elasticity of demand in this scenario in comprehensive detail.
Price elasticity of demand refers the responsiveness of quantity demanded with respect to price rise. It shows how the quantity demanded changes when there is a change in price. If the students still bought their favourite empanadas irrespective of price rise. Despite a strong branding, students are not willing to buy my products. Thus, the current demand for my empanadas are relatively elastic. A demand is said to be elastic when the elasticity coefficient becomes greater than 1.
Students have good substitutes of my empanadas in the market and tend to buy from them. If the price of empanadas has increased by 50%, the quantity demanded for my empanadas has come own by more than 50%, say 60%. The coefficient of demand elasticity becomes greater than 1.
PED = % change in quantity demanded/ % change in price
PED = 60%/50% = _________________________________
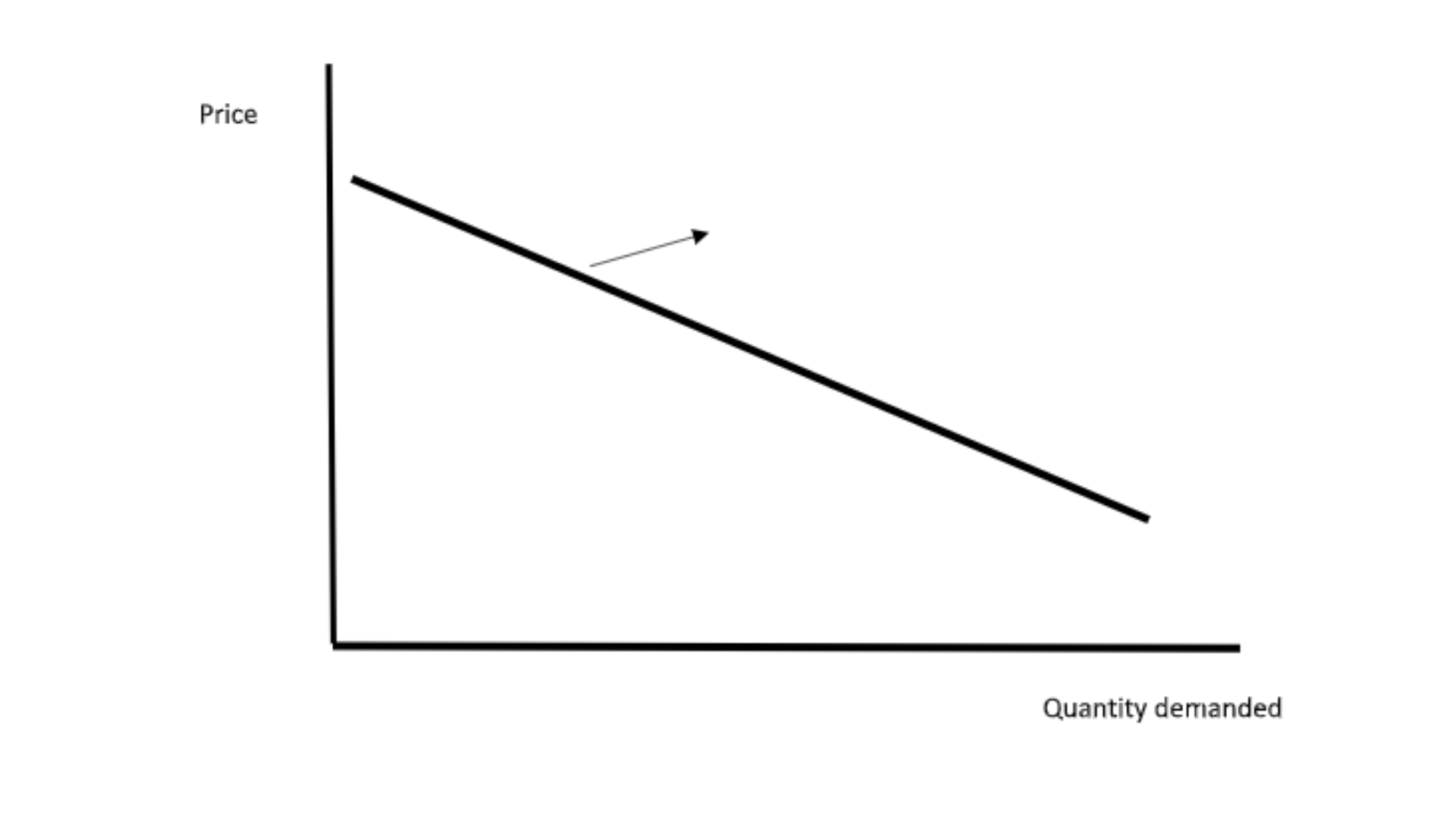
We can illustrate the elastic demand for our empanadas with the help of following diagram. The demand curve is flatter for elastic demand.
Get answers to your study questions for BLAW1002 from Business Law Experts. Call us today to know more- +61 871501720.
Question 4
Lastly, considering all the above factors, it has been assessed if the company could survive a price hike this extreme. Our experts have discussed the responses in terms of the creative rivals, the entrepreneur’s function, and the potential for excess profit when market entry barriers are high versus low. You can read a snippet of the complete answer written by our experts below:
Excessive price increase is not sustainable due to several reasons. A firm can charge higher price only if it has monopoly power. Monopoly firms can raise the price and earn huge profit. But other firms like the firm who is selling empanadas to the students can not sustain with higher price. This is because if the price remains high for a substantial period, then consumers will move to other firms and buy from them. They will even search for substitute products at competitive price. Consumers will choose to buy similar products at cheaper rate. Overtime, the innovative competitors would enter the market and grab the market share.
Want Economics Principles Analysis Assignment Help? Reach out today- onlineassignmentservices1@gmail.com.


